If you’ve been researching the crypto industry and crypto investments, you must have come across Bitcoin in your search. Bitcoin is the first cryptocurrency and most traded digital currency that powers peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries (such as traditional banks).
Over time, Bitcoin has become increasingly popular, and user adoption has encouraged more investors to consider investing in BTC. If you’re on this boat, it is only right that you understand the ins and outs of the crypto industry before investing.
Therefore, this article covers what Bitcoin is and how it works, its history, use cases, and Bitcoin mining. Additionally, we will show you how to buy BTC and the risks and challenges accompanying Bitcoin investments.
What is Bitcoin and How Does it Work?


Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency that operates on a peer-to-peer network without a central authority. It works using a public distributed ledger called the blockchain, which records Bitcoin transactions in chronological order. Each transaction is validated by a network of computers (nodes) through cryptographic proof, preventing fraud.
The blockchain is composed of blocks, each containing a batch of verified transactions and a cryptographic hash linking it to the previous block, forming a secure chain.
To add a block to the blockchain, a process called mining occurs, in which specialized computers solve complex computational puzzles (proof-of-work). Mining not only confirms transactions but also secures the network and rewards miners with new bitcoins.
However, over the years, Bitcoin mining has become more expensive. This is due to the significant increase in the network’s computational power (hashrate) and the resulting energy consumption. The hashrate nearly doubled recently, leading to more machines competing to mine fewer new Bitcoins.
One of the reasons for this is Bitcoin’s halving events, which reduce the block reward over time. Hence, miners must run more powerful hardware to solve complex cryptographic puzzles, and this requires more electricity.
Currently, mining a single Bitcoin consumes about 854,400 kilowatt-hours of electricity, which is equivalent to the annual power use of over 81 US households. The total electricity used to mine Bitcoin daily is immense, accounting for additional overhead such as cooling and infrastructure inefficiencies.
This surge in energy demand drives up operational costs, with electricity accounting for 60-80% of miners’ expenses. As a result, smaller, less efficient miners are pushed out, with mining concentrating among large-scale operations that have access to cheap or renewable energy sources.
Who Created Bitcoin?
Bitcoin was created by an individual or group using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. Nakamoto introduced Bitcoin to the world in a 2008 whitepaper titled “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System,” which described the concept of a decentralized digital currency operating without central authority.
The History and Evolution of Bitcoin
Bitcoin’s history began in 2008, when an anonymous person or group, using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto, published a white paper describing the network and its operation. After this, the Bitcoin network was launched on January 3, 2009, when Nakamoto mined the genesis block.
This was the first block on the Bitcoin blockchain, and it had an embedded message referencing the financial crisis and symbolizing a new vision for decentralized finance. The first Bitcoin transaction occurred later in 2009, when Nakamoto sent 10 Bitcoins to computer scientist Hal Finney.
In 2010, Bitcoin gained real-world value when a user bought two pizzas for 10,000 BTC. This event is now celebrated annually as Bitcoin Pizza Day. The following years saw the rise of exchanges like Mt. Gox, which played a crucial role in Bitcoin’s early adoption. Although the exchange eventually collapsed due to hacks.
Bitcoin evolved from a niche digital currency into a widely recognized financial technology. Over the years, it has led to the creation of thousands of alternative cryptocurrencies (altcoins) and hundreds of blockchain-based projects.
Bitcoin’s Role in Shaping the Cryptocurrency Industry
Bitcoin has played, and continues to play, a foundational role in shaping the entire cryptocurrency industry. It introduced the concept of a decentralized virtual currency based on blockchain technology.
Bitcoin set the standard for security, transparency, and decentralization that many other cryptocurrencies now replicate or improve upon. In fact, Bitcoin’s market dominance influences altcoin prices and trading volumes. Many investors use it as a benchmark or gateway into the crypto market.
The Technology of Bitcoin’s Blockchain


The technology behind Bitcoin’s blockchain is a decentralized, public ledger maintained by a P2P network of computers, called nodes. Here is a breakdown of the technology behind Bitcoin’s blockchain and why encryption is an invaluable part of the ecosystem.
Blockchain
Bitcoin’s blockchain operates without a central authority. It relies on a proof-of-work (PoW) mechanism to secure the network and prevent double-spending. To add new blocks, miners compete to solve computationally difficult cryptographic puzzles. The first miner to find a valid solution earns the right to add a new block of transactions to the blockchain.
This process confirms transactions and rewards miners with new Bitcoin, creating an incentive encouraging miners to continue securing the network.
The network automatically adjusts the mining difficulty roughly every two weeks to ensure that new blocks are added at a steady pace, regardless of the total mining power.
For transactions, Bitcoin uses elliptic curve cryptography (ECC) to generate private–public key pairs. This allows users to prove ownership and securely sign transactions.
The transactions follow the UTXO model, where each transaction consumes previous outputs and creates new ones. With this, every coin can be traced back through the chain.
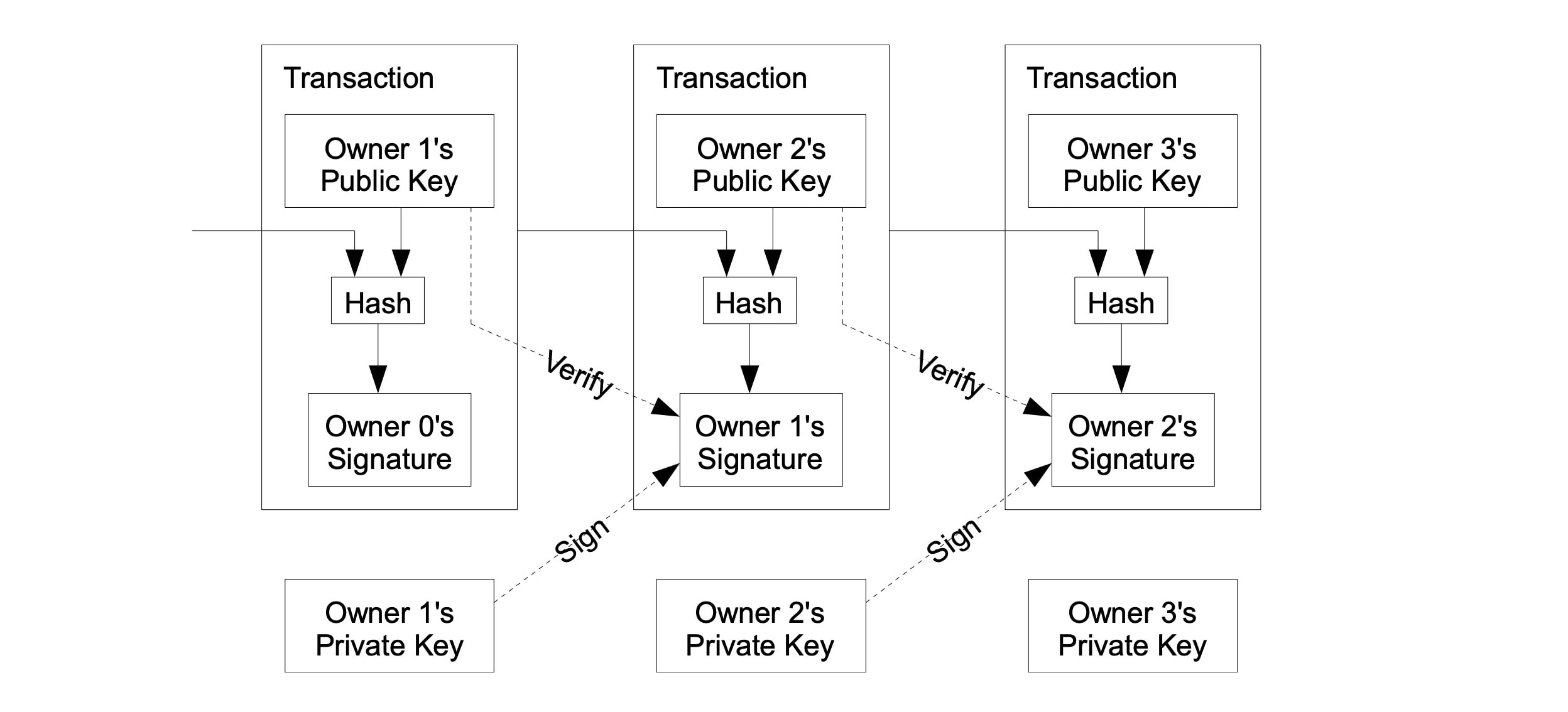

Because full nodes store the entire blockchain from the genesis block onward, every transaction in Bitcoin’s history remains publicly verifiable. This preserves the network’s transparency, security, and immutability.
Encryption
Blockchain technology relies heavily on encryption to ensure the security, integrity, and privacy of data stored and exchanged within it. Encryption transforms data into an unreadable format to protect it from unauthorized access.
There are two key ways encryption is applied in blockchain:
- Hash Functions: Blockchain uses cryptographic hash functions, such as SHA-256 in Bitcoin, to convert data into fixed-length, irreversible hash values. These hash values link blocks together in a chain, ensuring immutability. So any change in a block would alter its hash and break the chain. This protects data integrity and prevents tampering across the blockchain.
- Public Key Cryptography: Blockchain employs asymmetric encryption, where each user has a public and private key pair. The public key acts as the receiving address, while the private key signs and authorizes asset transfers. Digital signatures verify transaction authenticity and ensure only the rightful owner can spend the assets.
These encryption techniques used by blockchain secure transactions and data communication. They also help maintain the trustless and decentralized nature of blockchain, and enable encryption of sensitive on-chain data.
What Is Bitcoin Used For?
Bitcoin is a major part of the decentralized ecosystem, offering many use cases that other altcoins draw inspiration from. Some of Bitcoin’s use cases include:
- Peer-to-Peer Payments: Bitcoin enables direct electronic payments between people anywhere in the world without the need for intermediaries like banks, allowing fast, borderless, and currency conversion–free transactions.
- Investment and Speculation: Many people buy and hold Bitcoin as a long-term investment or trade it for profit on cryptocurrency exchanges, viewing it as a hedge against traditional financial markets.
- Crowdfunding: Bitcoin enables global crowdfunding without third-party involvement, allowing projects to raise funding from worldwide supporters without currency conversion.
- Online Gambling: Some gambling platforms, especially crypto gambling sites, accept Bitcoin for deposits and withdrawals, offering faster, cheaper, and more private transactions.
- Purchasing Goods and Services: Businesses across industries accept Bitcoin payments, enabling customers to buy products and services quickly and cheaply, regardless of location.
- Remittances: Bitcoin enables sending money across borders more efficiently and cheaply than traditional remittance services.
What Is Bitcoin Mining and How Does It Work?
Bitcoin mining is the process by which new bitcoins are introduced into circulation and transactions are verified and added to the blockchain. Miners use powerful computers to solve complex cryptographic puzzles, known as proof-of-work, which involve finding a hash that meets specific criteria.
When a miner successfully solves these puzzles, they validate a new block of transactions, add it to the blockchain, and are rewarded with newly minted bitcoins and transaction fees. This process supports the network’s security and integrity by preventing fraud and maintaining transparency.
However, Bitcoin mining is not generally accessible due to the high costs. Mining BTC requires specialized hardware, such as ASICs (application-specific integrated circuits), which perform the SHA-256 hashing algorithm to rapidly generate and test potential solutions. The process is competitive, with miners worldwide competing to solve the puzzle first.
The decentralized nature of mining ensures no central authority controls the Bitcoin network. Meanwhile, the issuance of new bitcoins follows a halving schedule that reduces block rewards approximately every four years to control inflation.
How Do You Buy Bitcoin?
For crypto investors who aren’t miners or don’t have access to mining hardware, the way to own BTC is to buy it. Follow these straightforward steps to buy Bitcoin.
- Choose a Wallet: Decide which type of wallet you will use to store your Bitcoin. You can choose a software or hardware wallet if you prefer to store your BTC offline.
- Select a Crypto Exchange: Choose a reputable crypto trading platform or exchange that supports Bitcoin transactions based on fees, security, and user experience. You can opt for either centralized (CEXs) or decentralized crypto exchanges (DEXs), depending on your trading goals and requirements.
- Create an Account: Sign up on the chosen exchange by providing personal information and completing KYC verification (especially for CEXs), including uploading a government-issued ID and possibly proof of address.
- Deposit Funds: Add fiat currency to your exchange account using supported payment methods such as bank transfer, credit/debit card, or e-wallet. You can also fund your account by transferring Bitcoin from another wallet if you already have one.
- Place an Order: Go to the trading section, select Bitcoin trading pair (e.g., BTC/USD or BTC/USDT), choose order type (market order for immediate purchase or limit order to specify a price), enter the amount, and confirm the purchase.
Aside from this process, many exchanges offer P2P marketplaces, where traders can buy BTC directly from other investors using local payment methods. All you have to do is create your account and navigate to the P2P Trading section, then select an ad and add details of your trade to proceed.
How to Store Bitcoin Safely
To store and use Bitcoin safely, the key is choosing the right type of wallet and following security best practices. Here’s how to go about it:
- Hardware Wallets: These are crypto wallets that store BTC offline. These wallets offer the highest security for long-term storage by keeping private keys offline. Examples include Ledger Nano X, Trezor Model T, and Tangem Wallet. They are highly resistant to hacking, malware, and phishing attacks because private keys never leave the device.
- Cold/Offline Wallets: Similar to hardware wallets, these are fully offline (e.g., paper wallets or hardware devices) and ideal for storing large amounts of Bitcoin over the long term. Even exchanges use these types of wallets to store the majority of user financial assets, safeguarding them from security breaches.
- Hot Wallets: Hot or software wallets are connected to the internet, making them suitable for frequent financial transactions but more vulnerable to security threats. Examples include non-custodial wallets such as Trust Wallet and Metamask. Setting up these wallets is easy; here is a detailed guide to setting up a MetaMask wallet.
- Custodial Wallets: These wallets are centralized exchanges that enable traders to buy, hold, trade, and sell Bitcoin, with the platform acting as an intermediary. They are convenient, but they require users to trust the provider for security and transparency.
Is Bitcoin a Good Investment?
Bitcoin can be a good investment in 2025. The cryptocurrency has shown consistent price increases over the years, hitting an all-time high of $126,198.07 in October 2025. Seeing the steady growth over the past decade, many analysts and investors remain optimistic about Bitcoin’s potential. Therefore, predicting significant price increases in the next few years.
However, Bitcoin is highly volatile, and its price can decline sharply. For instance, the all-time high status from October didn’t last long as the price of BTC dipped to 89,000 the following month. So if you’re considering investing in Bitcoin, prepare for potential volatility and treat it as a long-term investment rather than a quick profit vehicle.
Risks and Challenges of Investing in Bitcoin
While there are many advantages to investing in BTC, it also carries associated risks and challenges, which we’ve highlighted below.
- High Volatility: Bitcoin prices are highly volatile, with large price swings that can lead to significant financial losses if investors sell during downturns. This volatility is higher than that of traditional assets like stocks, bonds, or gold, requiring a long-term perspective and a high risk tolerance.
- Security Concerns: Risks from wallet hacks, fraudulent schemes, exchange vulnerabilities, and crypto theft are increasing by the day as scammers find new and advanced ways to access investors’ (both individuals and institutions) accounts, wiping out their balances.
- Market Manipulation: Bitcoin prices can be influenced by whales (large holders) and coordinated market moves, leading to unpredictable price shifts and potential manipulation.
- Complexity and Fees: Buying, storing, and securing Bitcoin requires some technical knowledge. Fees on exchanges and transaction costs can be higher than those of traditional financial services.
- Uncertain Long-Term Status: Despite growing adoption and strong use cases, it is unclear whether Bitcoin will maintain its current position or be supplanted by other technologies or regulatory changes in the next 10–15 years.
Bitcoin and the Future of Cryptocurrency
Experts predict Bitcoin has strong growth potential over the next decade, with many forecasts ranging from $150,000 to over $500,000 by 2030, depending on adoption and macroeconomic conditions.
Mass adoption of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies is also expected to skyrocket. Primarily due to increased use cases such as payments, remittances, and decentralized finance (DeFi) services. These newer projects are supported by improvements in scalability, privacy, and user experience.
Additionally, many countries accept crypto as a legal tender and part of a national reserve strategy. For instance, President Donald Trump announced a Strategic Reserve that includes SOL, XRP, ETH, BTC, and more assets earlier in 2025.
Trump’s executive order reflects a shift in official policy towards embracing crypto assets at a strategic level. This can influence market sentiment, regulatory clarity, and infrastructure development in the cryptocurrency space.
In all these, challenges lie ahead, including regulatory scrutiny, innovation from competing blockchains, and scalability and energy consumption concerns.
Conclusion
Bitcoin has transformed various industries. It has improved cross-border payment processing and provided individuals and institutions with opportunities to store, buy, sell, and exchange digital assets.If you are considering investing in BTC, first understand the technology behind it. Then learn how to buy and trade easily and determine whether you have sufficient capital to buy a substantial amount. If your trading capital is insufficient, consider investing in other altcoins to boost your profits.
FAQs
Bitcoin is considered a new kind of money due to decentralization, fixed supply and scarcity, P2P payments, transparency, and immutability. Unlike traditional money, Bitcoin operates on a decentralized network of thousands of nodes worldwide, removing the need for central authority.
At the time of writing, 1 Bitcoin (BTC) is trading at approximately $89,800 USD. This reflects the latest market data, but Bitcoin’s price is highly volatile and can change rapidly within short time frames.
Since one Bitcoin is currently trading at $89,800 USD, investing $100 would give you approximately 0.001113 Bitcoin. This means you own roughly 0.1113% of one Bitcoin for your $100 investment at that price. Future gains or losses depend on Bitcoin’s price movement from that point, but your initial allocation is based on that ratio.
Yes, you can convert Bitcoin into cash through several channels, including crypto exchanges, Bitcoin ATMs, P2P platforms/marketplaces, and debit/credit cards via third-party payment processors.

