What is a wallet address? It is a unique identifier made of letters and numbers that helps you receive and send crypto on a blockchain. Its structure varies across cryptocurrencies as every network follows a unique wallet address format.
In this guide, we’ll delve deeper into crypto wallet addresses and their types. We’ll also provide a step-by-step guide on how to get a wallet address and safety tips to manage funds efficiently.
What Is a Crypto Wallet Address?
A cryptocurrency wallet address is a unique string of alphanumeric characters. Many addresses, especially those on Ethereum and EVM chains, are hexadecimal, meaning they consist of numbers 0-9 and letters A-F. Moreover, certain blockchains are case-sensitive (e.g., Solana) or may require a destination tag (e.g., Ripple).
How Does a Crypto Wallet Address Work?


A crypto wallet address is analogous to an email address. An e-mail ID helps you send and receive messages. Similarly, a wallet address enables you to send and receive crypto to and from other users.
To verify the security and authenticity of cryptocurrency transactions, wallet addresses leverage cryptographic algorithms. Additionally, these addresses are pseudonymous. They conceal your identity, enhancing anonymity and privacy.
When you create a wallet, the platform/application generates an exclusive address for you. Each crypto address comprises two critical components: a public key and a private key.
Public keys are comparable to bank account numbers that are specific to each user and can be shared with everyone. Private keys are akin to ATM PINs. They’re secret codes that must be kept confidential to prevent unauthorized usage of funds. Moreover, you require private keys to access the digital assets stored in your wallet, sign blockchain transactions, and decrypt data.
Cryptocurrency wallets automatically generate cryptographic key pairs (public and private keys) and store them securely. They use encryption algorithms to generate a public key from your private key. They also computationally derive a hashed and shortened version of your public key, which becomes your wallet address.
When you initiate a transaction, it’s verified by the network using cryptography and consensus protocols. However, assets transferred to the wrong wallet addresses can’t be recovered — always double-check before sending.
How to Create a Wallet Address?
Step 1: Select a crypto wallet


Based on your preferences, select a suitable blockchain wallet. If you want a third party to safeguard your funds, choose custodial wallets like Kraken or Gemini. If you want full control of your private keys, opt for non-custodial wallets like Metamask or Phantom. For offline storage of cryptocurrencies, consider hardware wallets such as Trezor or Ledger.
Step 2: Choose a digital asset
Depending on the cryptocurrency you’re about to receive, create a compatible wallet address. For example, you’ll need an Ethereum wallet address to receive ETH tokens.
Step 3: Generate a wallet address
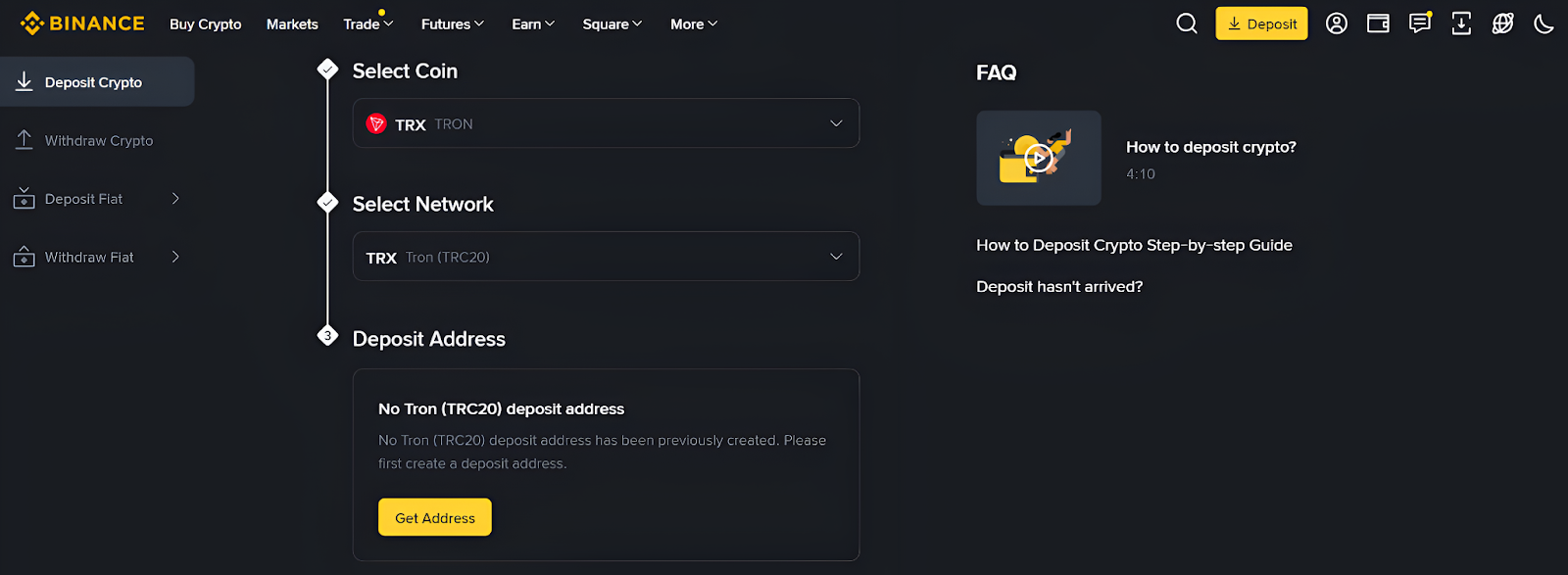

Imagine you want to create a Tron address to receive TRX tokens in your crypto wallet on Binance. To proceed, follow the steps below:
- Log on to your Binance account and click the “Deposit” tab.
- Select TRX coins and the TRC20 network.
- Click the “Get Address” tab. The wallet will instantly generate a TRC20 deposit address.
- Copy and share this address with the sender.
Types of Crypto Wallet Addresses
Bitcoin Wallet Addresses (BTC)
A Bitcoin wallet address is a distinct combination of letters and numbers used to execute BTC transactions. You need a Bitcoin-compatible wallet to receive BTC payments and interact with the Bitcoin blockchain. There are primarily three types of Bitcoin wallet addresses:
- Pay-to-Public-Key-Hash (P2PKH): This is the legacy script pattern and the original Bitcoin address structure, which begins with 1. It enables users to send Bitcoin (BTC) to the hash of a wallet’s public key, rather than the public key itself.
Example: “1FfmbHfnpaZjKFvyi1okTjJJusN455paPH”
- Pay-to-Script-Hash (P2SH): This address structure starts with 3 and allows you to lock BTC to a script hash, instead of a public key. It is compatible with both non-SegWit (P2PKH) and SegWit (Bech32) addresses.
For instance: “3J98t1WpEZ73CNmQviecrnyiWrnqRhWNLy”
- Bech32: These are the native SegWit addresses that start with “bc1”. Though they’re case-sensitive, they’re shorter and facilitate more efficient transaction processing. They help reduce crypto transaction costs considerably and have a built-in checksum to detect errors.
Example: “bc1qw508d6qejxtdg4y5r3zarvary0c5xw7kygt080”
Ethereum Wallet Addresses (ETH)
Ethereum addresses are 42-character alphanumeric strings prefixed with “0x”, helping users send/receive ERC-20 tokens and Ethereum-based digital assets. They support smart contracts, dApps, and DeFi protocols.
Example: “0x4e3b2a1F9C6D8B7E5A0F2cD91E8B4a6f3C7D2A9E”
Other Common Wallet Addresses
- Litecoin: LTC receiving addresses begin with an L or M and change automatically for every transaction in most crypto wallets.
- Solana: Solana addresses are 32-44-character Base58-encoded strings that act as unique identifiers on the SOL network.
- Cardano: An ADA address is created by hashing your public key using the Blake2b-224 algorithm. Usually, it uses the prefix “addr1”.
How to Find Your Wallet Address?
- Open your crypto wallet desktop/mobile application.
- Click the “Deposit” button and choose “Deposit crypto” from the dropdown menu.
- Select the token and network for which you want to find a wallet address. The address will be immediately displayed on the screen.
- Copy the address or scan the QR code carefully.
- Double-check if you’ve shared the correct address with the sender.
How to Send and Receive Crypto Using a Wallet Address?
To send cryptocurrencies to someone, you must first request their crypto wallet address. Once you obtain the necessary details, input the recipient’s address correctly in your wallet application or software. Specify the coin and amount you wish to send. Additionally, select the correct network.
The software/app will auto-calculate and display the network/gas fees you need to incur to execute a cryptocurrency transaction. Review the transaction details and fees. If correct, hit the “Confirm” tab. Your send transaction will now be broadcast to the network for verification. Once validated, the transaction will be recorded in a block and added to the blockchain.
To receive cryptocurrencies, you need to share your public wallet address with the sender. The sender will enter your address in their wallet app along with other details like token, amount, and network. Once the sender’s transaction is approved by the network, the funds will be credited to your wallet.
Is It Safe to Share Your Wallet Address?
Yes. It is absolutely safe to share your address with others. Moreover, you must disclose your wallet address to receive cryptocurrency payments. As long as your private keys and recovery phrases aren’t compromised, nobody can access your funds. Your identity or business name also remains hidden.
However, blockchain explorers like Etherscan, Solscan, and Polygonscan display the transaction histories linked to a particular public address. As cryptocurrencies are designed to record transactions on immutable, transparent ledgers, you can’t stop explorers from tracking your wallet activities.
To facilitate smoother crypto payments, organizations often display wallet addresses on their websites, QR codes, and invoices. For enhanced security, some businesses create unique addresses for each transaction.
Furthermore, self-custody wallet addresses grant you complete control over your private keys. They don’t require identity verification and are less prone to cyber attacks than custodial wallets.
How to Keep Your Wallet Address and Funds Secure?
- Choose renowned digital wallets: Always select well-known Web3 wallets with cutting-edge security features like multi-party computation, protection fund, etc. Before downloading a wallet app, check user feedback on reputable review platforms such as Trustpilot and Reddit.
- Store private keys offline: Backup your private keys in hardware wallets like Trezor and Ledger. As they aren’t connected to the internet, they aren’t exposed to online threats.
- Double-check transaction details: When you’re sending funds, ensure the transaction amount and the recipient’s wallet address are entered accurately. Also, check whether you’ve selected the right token. While receiving crypto, ensure you’ve shared the correct wallet address corresponding to the cryptocurrency you’re about to receive.
- Update wallet software: By regularly updating your wallet software, you’ll gain access to the latest features and security protocols. Wallets without the most recent updates are more susceptible to hacks.
- Enable multi-factor authentication: Most crypto wallets require users to undergo multiple levels of verification to access their funds. These include a secure password, e-mail verification, and a Google Authenticator code.
- Restrict transactions to whitelisted addresses: Many wallets, like Bitget and Coinbase, allow you to whitelist trusted wallet addresses. This feature serves as an additional security layer for your funds.
Common Wallet Address Mistakes to Avoid
- Transferring cryptocurrencies to the wrong addresses: If you send crypto to incorrect addresses, your funds will be lost forever, with zero chances of recovery.
- Copy-paste, typo, or scanning errors: Since wallet addresses are long and complicated, use domain name services to shorten them and avoid typing them manually. Even if a single character is missing in the address, you may lose your money. Either you’ll end up sending assets to the wrong recipient or fail to receive funds. Moreover, malicious QR codes often contain fraudulent addresses. Thus, whether you copy-paste or scan, double-check wallet addresses before initiating transactions.
- Sharing your private keys: Losing your private keys is akin to losing your crypto assets permanently. Therefore, never share your private keys with anyone and avoid storing them in software wallets.
- Using the same address for multiple transactions: As wallet addresses are publicly visible, generate a new address for each transaction. Avoid reusing the same wallet address repeatedly to deter scammers from fraudulently stealing your funds. If you want more anonymity, use hierarchy deterministic wallets. They automatically generate distinct addresses from a single recovery phrase.
Conclusion
Wallet addresses serve as destinations for receiving funds. They consist of a unique string of characters and are comparable to bank account numbers. Plus, each blockchain’s wallet address has its own format. In essence, understanding wallet addresses is key to choosing the right blockchain wallet for protecting your cryptocurrencies.
FAQs
Each blockchain has a unique address format. Typically, wallet addresses contain numbers and upper/lower case letters. An example of a wallet address would be “rP1Cosk2Z7v3T3h5N6yZJZyGqj1n5bX9K”.
No. Your wallet address is a hashed and shortened version of your public key. The hash makes your address shorter while ensuring it is linked to the correct key pair.
As cryptocurrency transactions are recorded on publicly verifiable blockchains, your wallet address can be traced. It is also possible to decode the real identity of users based on their wallet activities. However, without your private keys or recovery phrase, no one can access your funds even if they know your wallet address.
Whether your wallet address remains unchanged depends on the blockchain on which the crypto asset exists. For example, Ethereum addresses are static, while Bitcoin generates a new address for each transaction.
If you lose access to your wallet address, you can restore access using your recovery phrase or private key. However, if you’ve forgotten your private key and didn’t maintain a backup, your funds will remain inaccessible forever. Avoid such situations by enabling multi-user access controls, exporting seed phrases, and assigning admin-level retrieval options. Also, choose crypto wallets with built-in backup tools. For added security, create a new wallet address for every client/transaction and block suspicious addresses.
Your wallet address is like your bank account number or e-mail ID. Nobody can hack your wallet using your address, unless they get hold of your private keys or seed phrase.

